We spend almost 18-20 hours of our day indoors. Out of those, a substantial percentage belongs to the time we spend at our workplaces. Therefore, a healthy indoor environment is important to create a productive workspace. Read more to find out how indoor air quality relates to occupational health and safety.
What is occupational health and safety?
Occupational health falls under the domain of environmental health and safety as well as public health. It is the study of trends associated with the health and well-being of the workforce of a place. It also includes a management plan containing both preventive and mitigation strategies to deal with unfortunate incidences at the workplace at different levels. Occupational health and safety also chalk out regulations and allows the implementation of standards to provide a wholesome environment to the worker population.
The primary objective of occupational health and safety is to identify the potential risks and limit the occurrences of both short-term and long-term hazards. It is to ensure the comfort of the employees and enhance the productivity of the workplace.
Indoor Air Quality of a workplace
Indoor Air Quality of your office building holds more importance than you can apprehend. Breathing pure air at all times is everyone’s right. Not only does it maintain individual health, but it also creates a positive work environment. High concentrations of air pollutants sketch indoor air pollution as the antagonist which can perturb your physical as well as mental equilibria.
Indoor Air Quality is both a comfort and health parameter for an office. It directly alters the ease with which the workers perform their tasks and affects the overall productivity of the work environment.

Indoor Air Quality is both a comfort and a health parameter. Good air increases the productivity by up to 11%.
The most probable reasons that can throw the indoor air quality of your workplace off the balance are-
- Lack of, or poorly managed space
- Overcrowding
- Improperly managed or defect in the Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) system.
- Overrunning of moisture and dampness
- Accidental leakage
- The incursion of outdoor air pollutants through voids, crevices, ventilation system etc.
- Generation of indoor pollutants in internal processes and procedures
Health Impacts of substandard Indoor Air Quality
The effect of indoor air quality parameters differs according to the type of pollutant and the length of the exposure.
Short-term exposure to a large concentration of pollutants may give rise to a set of acute symptoms known as the Sick Building Syndrome. It leads the occupants to experience discomfort that can be linked to spending time in a particular building. The complaint may be localized (restricted to a room/specific area) or widespread {in the entire floor(s) or the building}. Sick Building Syndrome is usually common in old buildings or those that have been recently re-modelled/renovated.
Long-term exposure to a low concentration of pollutants can produce mild to symptoms like headache, dizziness, nausea, fatigue. It can impact your concentration levels by reducing your attention span and increasing the reaction time. So if you feel tired at your office for no reason or cannot concentrate on the computer screen, it might be because of the indoor air pollution. Yet you might not even know why!
Increased levels of air pollutants can also cause irritation in your eyes, nose, throat, and lungs. Prolonged exposure can even lead to organ damage. It cannot only adversely affect your lungs and heart, but can even be degenerative to your brain! Besides these typical symptoms, the deplorable indoor air quality of your workplace can cause diseases specific to some pollutants. For instance, asthma is associated with high levels of particulate matter.
Common Pollutants
 Numerous pollutants can hamper the air quality of your workplace depending upon the industry and the nature of your job. However, they fall under three basic categories :
Numerous pollutants can hamper the air quality of your workplace depending upon the industry and the nature of your job. However, they fall under three basic categories :
Biological Pollutants
These include the biological agents that can take advantage of the increase in moisture levels and creep into your office environment. Inadequate humidity control, accidental water spills, improper housekeeping, or leakage in the building can cause bacteria, viruses, fungi, pollen, dust mites, and animal dander to flourish.
These microbes can settle on the aerosol particles and remain suspended in the indoor air, making the occupants more susceptible to diseases.
Chemical Pollutants
These include the gases and vapours that can be detrimental to the occupational health of the workers. Their sources include the emissions from the products and installations in the building, such as furniture, office equipment, wall and floor coverings, cleaning products, and pesticides. Construction or renovation activities, accidental chemical spill, and combustion can also release the compounds that cause deteriorate the indoor air quality of your workplace.
Particulates
Particulate Matter (PM) is the suspended microscopic aerosol (solid or liquid) particles present in the air. PM 10 and PM2.5 are smaller than 10 micrometres and 2.5 micrometres in diameter respectively, out of which the latter is respirable. To put things into perspective, PM 2.5 is almost 1/30th of the size of a human hair ! These include the dust, dirt, and smoke resulting from the internal activities of the building. They can also diffuse in from ambient air outside through the ventilation system or the fenestration.
Sources that contribute to Indoor Air Pollution
Numerous sources can contribute to indoor air pollution at your workplace. The most typical sources include-
- Location of the building
- Infrastructural design of the building
- Renovation Activities
- Materials and Equipment
- Local Exhaust Ventilation
- Furnishings
- Maintenance of the building
- Activities of the occupant
The relative importance of a single source depends on the volume of pollutants it emits and the toxicity of the contaminant. It also depends on the closeness of occupants from the pollution-source and the efficiency of the ventilation system. The organization lays out the occupational health and safety management plan after carefully considering all these factors relevant to their workplace.
Monitoring Indoor Air Quality for Occupational Health and Safety
Air pollution affects all of us conspicuously. However, most of the time we remain unaware that the air around us is not breathable. We can easily spot, identify, and assess the impact of the physical impurities in things around us. But how can we evaluate something that we cannot even see?
It makes air quality monitoring very important. Especially in an indoor environment where we spend 80-90% of our day. It becomes even more necessary to keep a tab on the air quality of a workplace to increase the well-being, productivity, and cognitive function of the employees.
Efficient indoor air quality monitoring not only aligns with the objective of occupational health and safety but also takes your workplace one step closer to sustainability. Monitoring the indoor air quality is the first step to make an efficient occupational health and safety management plan. You can identify the trends in the concentration of the pollutants and plan mitigation measures to control the indoor air quality specific to your workplace.
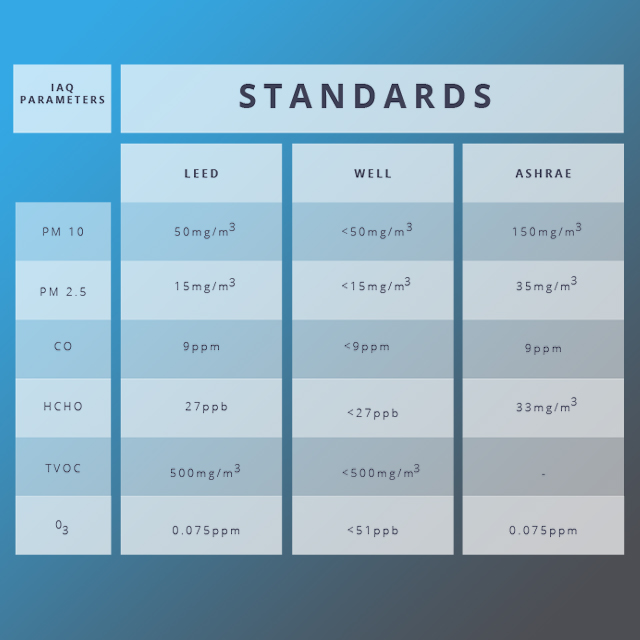
Indoor Air Quality Standards for a Green Building
Global certifications like Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design (LEED), WELL, and American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE) have laid down the standards for indoor air quality parameters. The administration of all the workplaces should adhere to those standards. Also, they help in creating a better indoor environment.